Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Futagami, Satoshi; Ando, Masanori; Yamano, Hidemasa
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/03
Onoda, Yuichi; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/05
The objective of this study is to develop an effectiveness evaluation methodology of the measures for improving resilience of nuclear structures at ultra-high temperature by using the failure mitigation technology. At the beginning, to identify the accident sequences having the potential to improve resilience, the characteristics of a next-generation loop-type sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR) in Japan has been investigated by analyzing the event tree of level-1 and level-2 probabilistic risk assessment. As a result, event sequences of loss of heat removal systems (LOHRS) are identified. The effectiveness of the measures for improving resilience is evaluated by quantifying the reduction rate of core damage frequency before and after the introduction of the measures for improving resilience for all the accident sequences leading to LOHRS. To examine applicability of the developed methodology, a trial evaluation has conducted for a next-generation loop-type SFR in Japan. Through the applicability examined, the method for the effectiveness evaluation was developed successfully. The refinement of the conditional success probability of the measures for improving resilience is the future work.
Tsuji, Mitsuyo; Aizawa, Kosuke; Kobayashi, Jun; Kurihara, Akikazu
Proceedings of 12th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS12) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2022/10
In sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs), decay heat removal after a core disruptive accident (CDA) is an important issue for the safety enhancement. Therefore, water experiments using a 1/10 scale experimental apparatus (PHEASANT) that simulates the reactor vessel of an SFR are conducted to investigate the natural circulation phenomena in the reactor vessel. In this study, experiments under the operation of the dipped-type DHX were conducted to investigate the effect of the heat generation ratio between the fuel debris on the core catcher in lower plenum and the reactor core remnant on the natural circulation behavior in the reactor vessel. The temperature distribution and the velocity distribution were measured under two heat generation conditions. Thus, the effect of the heat generation ratio between the fuel debris in the lower plenum and the reactor core remnant on the natural circulation behavior was quantitatively grasped under the dipped-type DHX operating conditions.
Onoda, Yuichi; Nishino, Hiroyuki; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2021 (ASRAM 2021) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2021/10
The effectiveness evaluations technology of the measures for improving resilience by applying a fracture control concept under ultra-high temperature conditions has developed for prototype sodium-cooled fast reactor Monju as a model plant, and the trial evaluation has conducted using this technology in this paper. The important accident sequences to which the fracture control concept is expected to be applied under ultra-high temperature condition are identified by investigating the results of the existing researches of level-2 probabilistic risk assessment for Monju. Accident sequences categorized in protected loss of heat sink and loss of reactor level are both identified as such important accident sequences which has the potential to prevent core damage. This study has developed the technology to evaluate the effectiveness of improving resilience, where the headings which stand for success or failure of the measures to improve resilience are introduced into the event tree, the branch probability of them is set, and the effectiveness of improving resilience is expressed as the reduction of core damage frequency. As a result of the trial evaluation of the effectiveness for the measures to improve resilience, it is confirmed that core damage frequency can be reduced by applying fracture control concept. The branch probability of the measures to improve resilience proposed in this study is tentatively assigned based on the assumption. This value is expected to be quantified by the forthcoming analyses of the integrity for the reactor vessel structure at ultra-high temperature. The technology developed in this study will be applied for the evaluation of improving resilience of the next generation sodium-cooled fast reactor.
Hourcade, E.*; Curnier, F.*; Mihara, Takatsugu; Farges, B.*; Dirat, J.-F.*; Ide, Akihiro*
Proceedings of 2016 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2016) (CD-ROM), p.1740 - 1745, 2016/04
In the framework of the French-Japanese agreement signed in 2014, CEA, AREVA NP, JAEA, and MHI/MFBR is jointly performing components design of ASTRID such as Decay Heat Removal Systems (DHRS). This paper is giving highlights of ASTRID DHRS current strategy. Focus is made on operating temperature diversification for in-vessel heat exchanger as well as core catcher coolability by an original features such as heat exchanger located within reactor cold pool, whose design was taken over by Japan team since 2014.
Oyama, Naoyuki; Gohil, P.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Kamiya, Kensaku; Leonard, A. W.*; Loarte, A.*; Maingi, R.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A171 - A181, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:82 Percentile:92.04(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Hubbard, A. E.*; Kamiya, Kensaku; Oyama, Naoyuki; Basse, N.*; Biewer, T.*; Edlund, E.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Lin, L.*; Porkolab, M.*; Rowan, W.*; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A121 - A129, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:45.96(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Dedicated experiments were carried out to compare the properties, fluctuation behaviour and access conditions of these regimes. A common shape was developed which scaled the plasma boundary except for aspect ratio. Scans of density and input power were carried out at several values of q95, so as to achieve ranges of dimensionless parameters. A striking similarity of access conditions was seen. These results suggest common physical mechanisms for the H-mode regimes, which do not depend critically on aspect ratio over this range. On the other hand, several differences in the details of the edge fluctuations were found, and will be reported. The effect of wall conditioning via boronization on the H-mode regimes will also be discussed.
Kamiya, Kensaku; Oyama, Naoyuki; Ido, Takeshi*; Bakhtiari, M.*; JFT-2M Group
Physics of Plasmas, 13(3), p.032507_1 - 032507_9, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:43.82(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Accompanying the HRS H-mode transition, the coherent magnetic fluctuations in the frequency range of the order of 10-100 kHz with significant variation are seen on the magnetic probes at the vessel wall. Above all, two types of edge MHD activities, which have associated toroidal mode number of n=1 and n 7, respectively, seem to be more important for the HRS H-mode plasmas. To investigate their interaction, bi-spectral analysis is applied for the magnetic probe data. It is found to be a powerful tool, exhibiting the phase-coupled oscillations between two types of edge MHD activities having n=1 and n
7, respectively, seem to be more important for the HRS H-mode plasmas. To investigate their interaction, bi-spectral analysis is applied for the magnetic probe data. It is found to be a powerful tool, exhibiting the phase-coupled oscillations between two types of edge MHD activities having n=1 and n 7.
7.
Kamiya, Kensaku; Oyama, Naoyuki; Miura, Yukitoshi; Hubbard, A. E.*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 46(11), p.1745 - 1755, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:40.12(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Recent experiments in the JFT-2M tokamak have concentrated on the studies of the access condition for the H-mode operation without any large ELMs, namely High Recycling Steady (HRS) H-mode regime in terms of the pedestal parameters. The HRS regime is more likely at the higher edge density and lower edge temperature, while the ELMy H-mode having large ELMs appears at the lower edge density and higher edge temperature. It is found that the ELMy/HRS operational boundary occurs at the normalized electron collisionality of  *
*
 1 in the plasma edge region, depending slightly on q
1 in the plasma edge region, depending slightly on q . A key feature of the HRS H-mode is the presence of the coherent magnetic fluctuations in the frequency range of the order of 10-100 kHz. It is suggested that the edge MHD activities may keep an edge pressure below a certain level needed to induce a large ELM.
. A key feature of the HRS H-mode is the presence of the coherent magnetic fluctuations in the frequency range of the order of 10-100 kHz. It is suggested that the edge MHD activities may keep an edge pressure below a certain level needed to induce a large ELM.
Kawashima, Hisato; Uehara, Kazuya; Nishino, Nobuhiro*; Kamiya, Kensaku; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Bakhtiari, M.; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Suzuki, Sadaaki; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 80(11), p.907 - 908, 2004/11
A comparison of divertor heat load between ELMy and "High Recycling Steady" (HRS) H-mode was carried out by fast measurements of the two dimensional 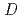
 emission, and the divertor electron temperature and ion saturation current on JFT-2M. They brought an attractive feature of HRS H-mode that the heat load was reduced to the level on time average that for ELMy H-mode, being able to avoid the severe heat load during pulsed ELM event. It was also indicated that the HRS H-mode was dominated by an enhancement of particle transport, whereas both heat and particle transport increased abruptly at ELM event.
emission, and the divertor electron temperature and ion saturation current on JFT-2M. They brought an attractive feature of HRS H-mode that the heat load was reduced to the level on time average that for ELMy H-mode, being able to avoid the severe heat load during pulsed ELM event. It was also indicated that the HRS H-mode was dominated by an enhancement of particle transport, whereas both heat and particle transport increased abruptly at ELM event.
Ishida, Shinichi; JT-60 Team; JFT-2M Group
Physics of Plasmas, 11(5), p.2532 - 2542, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:57.76(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Kensaku; Bakhtiari, M.; Kasai, Satoshi; Kawashima, Hisato; Kusama, Yoshinori; Miura, Yukitoshi; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Oyama, Naoyuki; Sato, Masayasu; Shinohara, Koji; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 46(5A), p.A157 - A163, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:56.33(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A new operating regime, High Recycling Steady (HRS) H-mode regime, has been discovered on JFT-2M, which is easily reproduced under the wall fueling from the boronized first wall. Accompanying the HRS H-mode transition, the coherent magnetic and floating potential fluctuations are seen on magnetic probes at vessel wall and Langmuir probe in SOL, respectively. These coherent fluctuations have a frequency of the order of 10-100 kHz with significant variation, which is recognized to be important to enhance the particle transport. The HRS can be seen even at 

 3 with
3 with 
 /
/
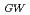
 0.4 for the fixed delta
0.4 for the fixed delta 0.4 in the standard single-null divertor configuration. Recent experimental results from JFT-2M show that the plasma shape also seems to play an important role in determining the type of ELMs. The HRS regime can be extended up to delta
0.4 in the standard single-null divertor configuration. Recent experimental results from JFT-2M show that the plasma shape also seems to play an important role in determining the type of ELMs. The HRS regime can be extended up to delta 0.75 and
0.75 and 

 2.6 in the double-null configuration, while lower delta boundary exists at delta
2.6 in the double-null configuration, while lower delta boundary exists at delta 0.3 with moderate
0.3 with moderate 

 4 even at high recycling and/or density condition of
4 even at high recycling and/or density condition of 
 /
/
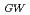
 0.4.
0.4.
Futagami, Satoshi; Ando, Masanori; Yamano, Hidemasa; Kasahara, Naoto*
no journal, ,
To improve resilience of next-generation nuclear power plants, the authors have performed a structural analysis assuming a protected loss of heat sink event, which may cause all decay heat removal systems to lose their functions immediately after reactor shutdown. The results show how the reactor vessel and guard vessel deform under extremely high temperatures.
Futagami, Satoshi; Ando, Masanori; Yamano, Hidemasa; Kasahara, Naoto*
no journal, ,
To improve resilience of next-generation nuclear power plants, the authors have performed structural analyses assuming a protected loss of heat sink event, which may cause all decay heat removal systems to lose their functions immediately after reactor shutdown. From the results of these analysis, the authors developed a passive safety structure under extremely high temperatures.